
Maternal depression increases children’s risk of cognitive, emotional, and behavioral problems, 2– 4 and treatment improves not only maternal symptoms but also child outcomes. 1 Once only a concern for mental health providers and obstetricians, maternal depressive symptoms are now firmly in the purview of pediatricians.


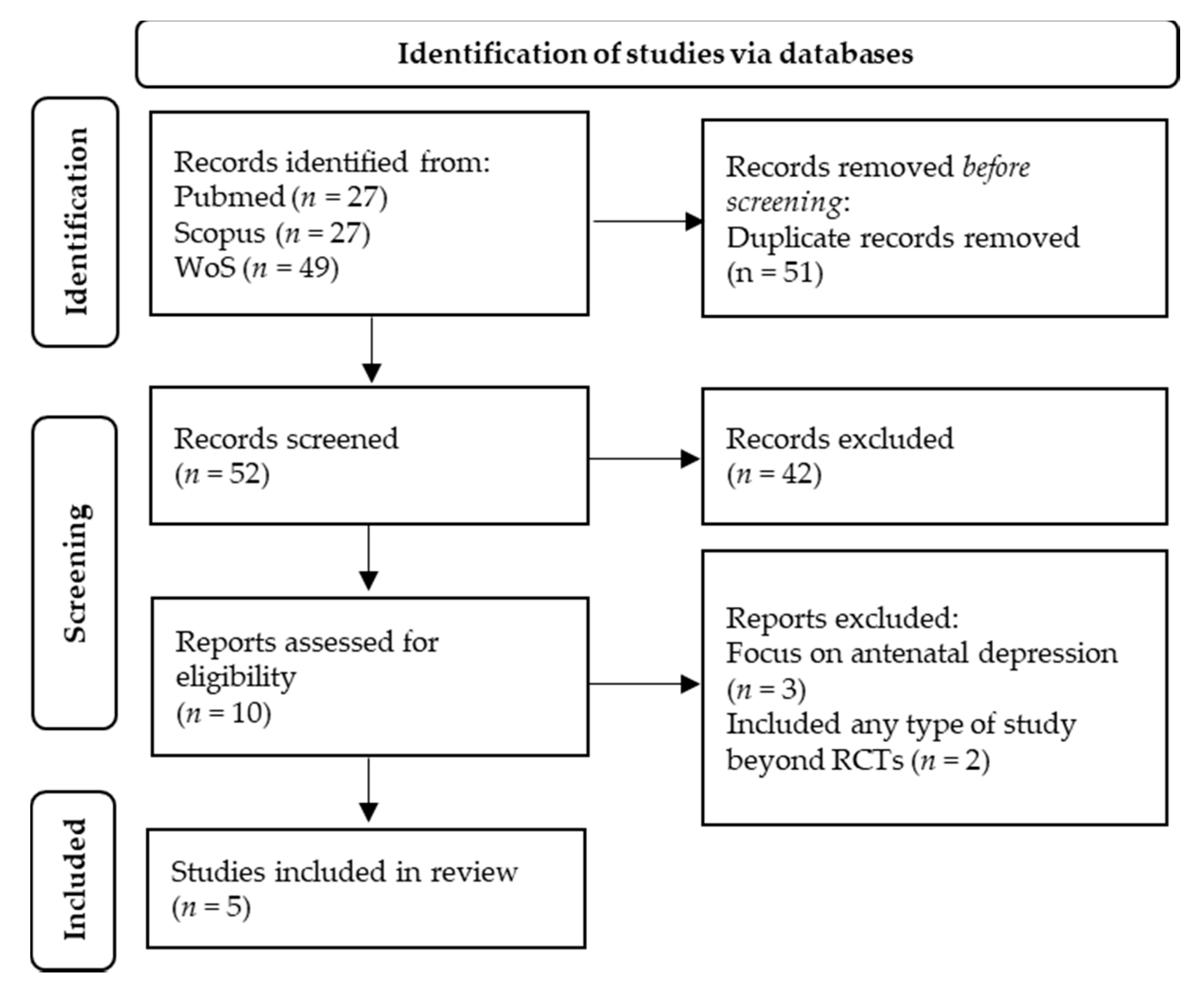
Recently, the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) recommended that primary care pediatricians screen for maternal depression at children’s 1-, 2-, 4-, and 6-month well visits. Infertility treatment, multiple births, prepregnancy BMI, gestational hypertension, and infant sex were not differentially associated with depressive symptom trajectories.
Compared with the high-persistent group, older mothers (maximum odds ratio of the 3 comparisons: 1.10 95% confidence interval : 1.05 to 1.15) or those with college education (maximum OR: 2.52 95% CI: 1.36 to 4.68) were more likely to be in all other symptom groups, and mothers who had a history of mood disorder (minimum OR: 0.07 95% CI: 0.04 to 0.10) or gestational diabetes mellitus diagnosis (minimum OR: 0.23 95% CI: 0.08 to 0.68) were less likely to be in other symptom groups. Four depression trajectories were identified: low-stable (74.7%), characterized by low symptoms at all waves low-increasing (8.2%), characterized by initially low but increasing symptoms medium-decreasing (12.6%), characterized by initially moderate but remitting symptoms and high-persistent (4.5%), characterized by high symptoms at all waves.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
